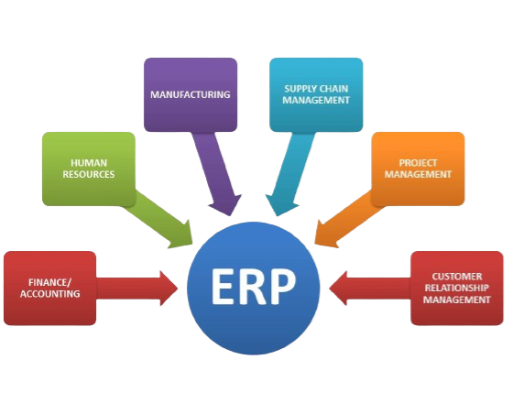
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a comprehensive software system that integrates various business processes and functions within an organization into a single unified platform. The primary purpose of ERP is to enhance operational efficiency, streamline data flow, and provide real-time, data-driven insights for making informed decisions. ERP systems typically cover various core functions, including finance, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain, customer relationship management, and more. Here are key aspects of ERP:
Modules and Functional Areas:
ERP systems consist of various modules, each designed to handle specific business functions. Common modules include financial management, human resources, procurement, inventory management, production planning, sales and distribution, and customer relationship management.
Integration:
Data Centralization:
Real-Time Information:
Process Automation:
Customization:
Reporting and Analytics:
Scalability:
Security:
Cloud-Based ERP:
Mobile Access:
Vendor and Open Source Solutions:
Implementation Challenges:
Return on Investment (ROI):
ERP systems have become a fundamental component of modern business operations, helping organizations of all sizes and industries manage their resources more effectively and stay competitive in an increasingly complex and data-driven business environment.